The nitrogen in the NR is mainly derived from the crude protein in the latex. Protein has a great influence on the properties of rubber. On the one hand, its decomposition products can promote the vulcanization of rubber, delay aging, and make rubber products durable; on the other hand, it can increase the water absorption, electrical conductivity, and heat generation of rubber. Insulating electrical equipment is manufactured to affect dynamic performance. Therefore, it is important to determine the nitrogen content in NR. At present, the determination of nitrogen content in crude protein mostly uses the Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer. Both China's national standards and ISO standards adopt this method. The Kjeldahl method is a classical chemical analysis method, and the results are accurate and sensitive. However, there are disadvantages such as long analysis time, complicated process, and lack of safety in operation. This work uses an automatic nitrogen determination instrument to determine nitrogen content in NR and compare it with the Kjeldahl method. Four different samples were measured using the instrument method and the Kjeldahl method. The results are shown in Table 3. According to the results of Table 3: Related Instruments: Fiber Tester Handle Screwdriver, Screwdriver Sets, Long Handled Screwdriver, Plastic Handle Screwdriver NINGBO LUBAN ELECTRIC POWER TOOLS CO.,LTD. , https://www.aye-group.com
1 experiment
1.1 Reagents The test catalyst, mixing indicator, boric acid absorbing solution and titration hydrochloric acid standard solution are all prepared in accordance with the requirements in GB/T 8088) 1999.
1.2 The main test equipment automatic nitrogen determination instrument, model KJELTEC 1030, Sweden FOSS products, with a nitrogen determination instrument distiller and automatic titration function, the smallest titration unit is 0.01 mL, according to the titration solution color change endpoint determination, distillation volume Up to 250 mL; Instrument equipped with a built-in thermostat digester, temperature control range of 50 ~ 440e. The digester volume for the analyzer is 250 mL.
1.3 Sample preparation Homogenize the test specimens according to GB/T 15340)1994[3].
1.4 Test methods
(1) Digestion Weigh 0.1-0.2 g (accurate to 0.000 1 g) of the sample into the digestive canal, add about 0.65 g of the catalyst mixture and 3 mL of sulfuric acid, and heat with the digester until the digestion solution is clear green and continue to boil for 30 min. Cool, add 75 mL of distilled water to be tested. At the same time do a blank test.
(2) Distillation and titration Set the lye pump stroke in the instrument to approximately 20 mL, the absorption pump stroke to approximately 15 mL, and the distillation volume to 140 mL. A blank test is performed first, and after the stable blank value is obtained, the digested sample is determined in order.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Determination of Distillation Volume Distillation volume refers to the volume of the smallest distillate under the premise of ensuring the complete distillation of the sample and accurate results. In the case of the determination of the experimental conditions, it corresponds to the distillation time. The determination results of nitrogen content of the same sample at different distillation volumes are shown in Table 1. 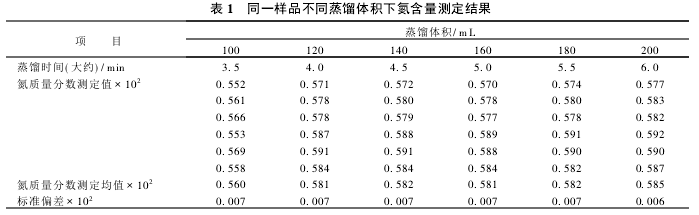
Since the nitrogen in the sample is digested with (NH4)2SO4, it is easily distilled under strong alkali conditions. From Table 1, it can be seen that when the distillation volume reaches 120 mL, the sample has been completely distilled. Therefore, the distillation volume is set to 140 mL and the distillation time is about 4.5 min. Although the distillation volume of the instrument method is 2 times that of the Kjeldahl method, the Kjeldahl method has a distillation time of 10 to 12 minutes and does not include the titration time. The instrument method is a simultaneous distillation and titration, so the test time can be Reduced by 2/3. 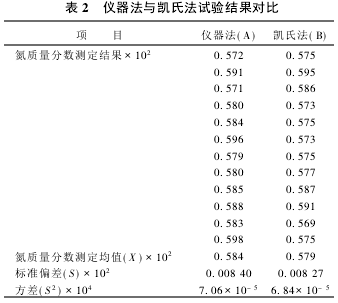
2.2 Significant test The nitrogen content of the same sample was determined using the instrument method and the Kjeldahl method, respectively. The results are shown in Table 2. According to the test results, the significance test was performed.
(1) F test 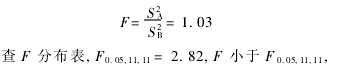 There was no significant difference in the variance between the two groups of data, and the precision of the two methods was the same.
There was no significant difference in the variance between the two groups of data, and the precision of the two methods was the same.
(2) t test 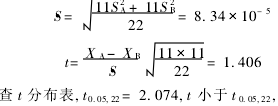 There was no significant difference in the results of the two assays.
There was no significant difference in the results of the two assays. 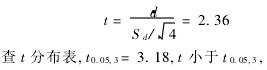 There is no systematic error between the two assays.
There is no systematic error between the two assays. 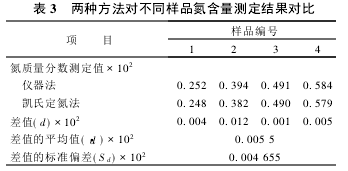
3 Conclusions The determination of nitrogen content in NR using an automatic nitrogen determination instrument has no significant difference from the Kjeldahl results. The test time can be shortened by 2/3. At the same time, due to the realization of electromechanical integration control, it can automatically control the temperature during digestion and shorten the digestion time. With the use of large digestive tubes, the sample does not foam, wall-climb, and paste during digestion, ensuring complete digestion of the sample; from digestion to distillation Titration without sample transfer process, the titration endpoint can be automatically identified, reducing the error caused by human factors.