The prevalence of wheat scab is fulminant and intermittent, and accurate prediction is the basis for good prevention and control. The forecast and forecast of head blight are mainly from the three aspects of bacteria source, wheat growth period and climate, and comprehensive analysis. The investigation of the bacteria source was divided into two groups, namely, the investigation of the bacterial colonization rate of ground piles and aerial spore capture. The aerial spores capture the spores using a microscopic method such as a quantitative air flow spore catcher wind direction catching method, an electric catching method, a fixed catching method, and a water dish method. The above methods are very time-consuming, and microscopic examination techniques are difficult and often difficult to find spores. Since 1978, we have conducted experiments to capture spores in the water plate agar culture method under the guidance of the Wheat Disease Group of the Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Through the 6-year experiment, it is preliminarily considered that the method has high prediction accuracy, labor saving and is simple and easy to implement. It is suitable to be used as a short-term forecast basis for the amount of bacteria to be surveyed at county-level or higher pest observation stations.
Martial Arts Mat is an EVA Mat, in double
colors for reversible, in 100cm x 100cm, offering 2cm, 2.5cm, 3cm and 4cm
thickness.
EVA martial arts mat is made from Eco-friendly, high
density, closed cell, non-smell and non-toxic EVA foam material. With
interlocking edges, each mat can be connected easily without any loose.
It is always used as EVA Tatami Mat, EVA Jigsaw Mat, EVA Taekwondo Mat, EVA Karate Mat, EVA Judo Mat, EVA Jiu Jitsu Mat and EVA Aikido Mat. The thick
foam provides a protection for trainers when they fall on the floor. Also we
have 3 different textures for surface of the mats, which is "T" texture, five
strips texture and tatami texture. All of them provide a good traction to the
feet.
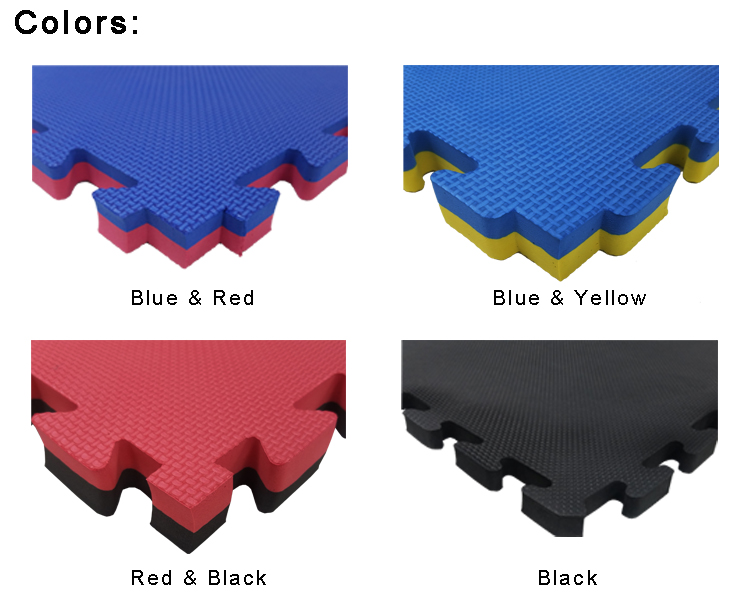
The
colors we usually offer for the martial arts mat is blue & red, blue &
yellow, black & red, single black. Or we can offer customized colors based
on customers` requirement.
We used
heard many of customers complained about the bad experience on the bad smell
mats they purchased from other supplier. Indeed, that may cost a lower even
half of our price, it is because the EVA foam material is what we call
second-hand material, its smell will make people uncomfortable. Melors promise
that the EVA foam material we use would be never second-hand foam material,
what we offer is truly non-smell and non-toxic.
Martial Arts Mat,Eva Martial Arts Mat,Eva Taekwondo Mat,Interlocking Jigsaw Mat,Tatami Interlocking Mat,Eva Karate Mat Huizhou City Melors Plastic Products Co., Limited , https://www.evaexpert.com
Water dish catch agar culture method Operation process (1) Preparation of culture medium. Wash the fresh potatoes (or sweet potatoes) and peel them, weigh 200g with a scale, cut them into fine granules, place them in a steel pot, add 1000ml of water, make a mark, boil for half an hour, and add a small amount of boiling water in the middle of boiling. Make it a total of not less than 10 ml. After cooking, use 4 layers of gauze to filter, to residue, add 20 g agar and 20 g of sugar in potato sap, boil again to dissolve all the agar, and add appropriate amount of boiling water to prepare 1000 ml of medium. After the agar and all the sugars are melted, they are placed in test tubes or conical flasks. Each tube is filled with about 18 to 20 ml. The test tubes and the flasks are stuffed with cotton, and the paper is sterilized by steaming in a pressure cooker or common pan. Wait for use later.
(b) Petri dishes, trays, induced seedlings. Select different types of 6 mound wheat fields, one for each hill. The water tray is a 10-cm-diameter petri dish that has been boiled and disinfected with boiling water. Use a special pencil to write the number or place a small label on the base. Use a 20-ml syringe to inject the sterile water. Each petri dish is 6-7. In milliliters, the bottom of the dish was spread over and placed on the wheat seeding platform at 4 o'clock in the evening, and was retrieved at 8 o'clock the next morning.
In front of the fungal trap, a small amount of _piling is used, which is about 80 cm from the ground. A 15×15 cm glass is placed flat on top of the mound. Three bamboos are used to support a 70 cm wide cap. Rain cover. The rain cover is 130 cm above the ground. In the past two years, the old bamboo was used to nail a board. The bamboo was buried 50 to 60 cm below the ground. The other distances were the same as above.
(c) The colony of the colony. After the prepared culture tube is boiled, it is placed in warm water to slowly cool the culture medium so as not to be hot. Add 2 drops of dihydrostreptomycin sulphate (500,000 units of dihydrostreptomycin sulphate plus 5 ml of distilled water in an eye drop bottle for use) in a Petri dish to induce bacterial water. Shake well and add cooling (around 45°C). The medium is rapidly shaken on the platen glass, covered with a petri dish lid, and placed in an incubator at 26° C. for 3 days. Observe to count the number of red roses.
Test results and discussion The results of the aerial spore prediction of Fusarium head blight in the water dish agar culture method for the six years from 1978 to 1983 were obtained and preliminary conclusions were drawn:
(1) The water tray catching agar culture method is labor-saving, the method is relatively simple, and it is superior to the method of capturing the ascospores of the agarose trap (I stand for 3 years). It can count the number of rose-red colonies produced by Fusarium head blight without microscopic examination, and it will not miss the number of spores captured. The requirements for disinfection and sterilization are not high. Even if there is growth of bacteria, it does not affect the inspection, so it is easy to spread. Promotion.
(b) The water tray agar culture method was used to capture air spores to predict the accuracy of wheat scab. According to statistical analysis, the correlation between the average number of colonies per plate in the first 10 days of the flowering period and early April in wheat and the incidence of heads of wheat scab was very significant and significant. The short-term prediction of wheat scab is obvious. Role (Table 1). We captured it with an electrospore catcher for 3 years. We caught very few spores and couldn't predict it at all. The investigation of the rate of prevalence of rice piles was conducted for 7 years. It was preliminarily believed that the rate of prevalence of rice piles was comparable to that of field wheat scab. There is no correlation in the degree of occurrence, so it cannot be used as a basis for forecasting the prevalence or not.
1. The relationship between the number of colonies per plate and the incidence of wheat scab in the first 10 days before the start of flowering in wheat was statistically significant (r=0.9563).
Table 1 The relationship between the amount of bacteria inoculated by water dish catching agar culture method and the incidence of wheat scab 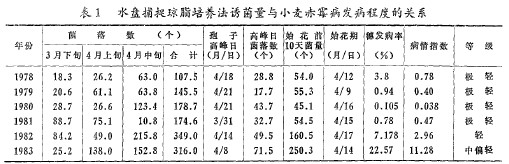
The y was the incidence (%) of wheat scab, and x1 was the average number of colonies per plate in the 10 days before the beginning of flowering. The predictive formula was:
y=0.09757x1 to 4.182±2.806
According to this formula, discriminating the average number of colonies per plate on the 10th day before the start of flowering in wheat was less than 100, and wheat scab was extremely light, generally not requiring the second treatment; in 100-250 years, it was a light year. Part of the wheat fields should be treated for the second time, 250 or more years for the hair, and the second should be treated. Therefore, this formula can be used to determine if wheat needs to be treated for the second time.
2. The relationship between the number of colonies per plate in the first half of April and the incidence of heads of wheat scabs was statistically analyzed. The results were statistically analyzed with 6-year data, and the correlation reached a significant level (r = 0.5225). The y is the incidence of head of wheat scab (intestine), x1 is the average number of colonies per plate in early April, and its prediction formula is:
y=0.1697x1 to 4.739±5.459
The initial period of wheat cropping in our county is about April 15th. Therefore, this formula can be used to predict the incidence of wheat scab in the short term and guide the first prevention and control work.
3. According to the results of the 6-year water tray catching agar culture method, the spore peaks of the 5 years were before and after the wheat was first flowered. The incidence of wheat in these 5 years was heavier than that of barley; in 1981, the spore peak day and the barley spike were particularly severe. The period was consistent, and almost no spores were caught since April 12, so the incidence of wheat ears in 1981 reached 5.7%, while the incidence of wheat ear was only 0.78%. This is very convincing about the relationship between bacterial count and disease.
From March 21 to April 20, the relationship between the average amount of induced bacteria per dish and the incidence of wheat head blight was not statistically significant, but the correlation was good. From 1978 to 1981, the amount of bacteria was less than 200 in 4 years, and the disease occurred in a very light year. In 1982-1983, the amount of bacteria was more than 300, and the disease occurred from mild to moderately mild years.