Copper oxide hydrometallurgical heap leaching
So far, mainly copper hydrometallurgical processing low-grade ore-based. Heap leaching (heap leaching) is the most important method of leaching of low grade copper oxide ore, generally refers specifically mined ores building heap leach operation, heap leaching a strict operating procedures. The leaching of waste ore produced by the process of exploiting mines, etc., is generally referred to as dump leaching, and its operating procedures are much simpler and more extensive. However, some scholars have dumped ore containing chalcopyrite, which has a long leaching period, also known as dump leaching .
        Pre-test face before building
        In order to properly understand the technical and economic indicators of heap leaching, adequate leaching chemistry and engineering tests are required prior to the implementation of the heap leaching project, which usually includes: determination of the mineral composition, composition, chemical and physical properties of the ore, such as total copper and acid. Copper grade, leachability, permeability, leaching speed, acid consumption, etc. The main parameters of the heap leaching that need to be determined are the ore particle size, spray leaching solution speed and stack height. The test methods mainly include column leaching and test heap leaching. However, some preliminary tests are to be done before the column immersion.
        In order to determine the leachability and acid consumption of acid-soluble copper in the ore, it is often used to grind the ore to 90%-200 mesh, and use a roller bottle or a stirred tank to carry out a leaching test under various acid addition amounts to obtain ore. The maximum leaching rate.
        During the leaching of the ore, the leaching solution penetrates into the ore through the pores and pores of the ore, and the dissolved metal also diffuses outward through the pores and pores. Therefore, the pores and pores of the nuggets determine the permeability and leaching speed of the nuggets. The permeation rate is not constant, but decreases exponentially with time, ie, the more slowly it moves into the nugget. Immersed in nugget with sulfuric acid, the initial speed is up to
        Column leaching test
        The column immersion test method is to fill the nugget in a hollow column, the leaching solution is dripped from the top of the column, flows through the nugget, and the leachate is collected from the lower outlet. This is very similar to heap leaching, so this method is often used to obtain design parameters for heap leaching and predictive evaluation of future production plants. The column immersion should be small and large and gradually enlarged.
        The contents of the column leaching are the effects of ore grade, particle size, acid concentration of the leachate and the spreading speed, column height and temperature on the leaching results. In addition to copper, the concentration of metals such as iron ( II ), iron ( III ) and cobalt and the acidity of the leachate should be noted . For example, copper sulfide minerals in the ore should also monitor the oxidation potential of the solution.
        De Ore Mantoux volts (Mantovorde) [1] is determined by the final column leaching nugget diameter of less than
Â
Copper leaching rate w ex ( Cu ) /% = 89.1% + 24.6ln[w t ( Cu ) /%]
Acid consumption A / ( kg · t-1 ) = 215.3 + 6.8w ( CaCO3 ) %
Â
        Heap leaching engineering design
        A heap size
        The overall size of the stack depends entirely on the overall production scale of the plant. However, in order to ensure the stable supply of the leachate, it is generally necessary to build about ten piles, which are divided into several groups, which are in various stages of pile-up, initial leaching and post-leaching.
        B ore particle size
        Although the main parameters such as the optimum particle size range, stack height, stack operation period, acid consumption and leaching concentration have been determined by column immersion test, some amplification correction factors must be introduced for these parameters during design. In order to be safe. This coefficient can be between 0.93-0.96 %, which is smaller in the first year and then increases year by year.
        For the ore particle size, the upper limit of the experimental value should be taken. The relationship between the particle size and the copper recovery rate is roughly as shown in the figure [2] . Chile's large copper factory St. Manuel adopts 90%

C pile height
        The height of the pile should be taken as the lower limit of the recommended value of the experiment, so as to shorten the operation cycle of the pile. When the initial work lacks experience, the actual operation experience can be obtained quickly, which is beneficial to the design and construction of the pile in the future. St. Manuel adopts pile height
D spray speed
        The spray rate determines the total amount of leachate produced, which determines the size of the extraction plant. The spraying speed is of course advantageous for lower speeds, and reducing the total flow can reduce the investment, so that some room can be left on the basis of the column leaching results. Generally around 5-lOL/m 2 h [ 3] .
        Stacking engineering implementation
        According to the design requirements, the broken ore is piled up from one side to the other by a loader or dump truck to reach the specified height. Then use a track-type tractor to level the top. The slope of the pile is about 30 ° . As the vehicle is driven at the top, the pile becomes dense, the gap in the pile is reduced, and the pile structure is gradually destroyed, which is not conducive to uniform penetration of the solution and air flow. As a result, many mines use belt conveyors that are transported to the top of the yard and then leveled with bulldozers. Chile, according to Seoul · A Bola mine (El Abra, an annual output of copper, 215,000 t) and Leiduo Mi Qiao · Tuo Mike mine (Radomitro Tomic. An annual output of copper, 150,000 t) and other large industrial design and manufacturing expertise, a large The conveyor can move in both the vertical and horizontal directions to uniformly transport the mine to the yard. Due to the huge yard, a satellite positioning system is used to command the unloading position of the ore, which is very efficient and low in cost. The figure below is a schematic diagram of the immersion structure.

        Heap leaching operation
A heap of start
        Dip the leachate onto the heap, start leaching, and start the heap. For the new plant, the leaching agent used is a dilute sulphuric acid solution, so the dilute solution from the beginning of the new reactor is returned to the stack until the desired concentration is reached. When the copper content of the returned leachate is gradually stabilized, the composition of the leachate also reaches a design value, and the leachate at this time is called a leachate, and its concentration fluctuates within a certain range.
        B heap leaching operation
   During the leaching process, the copper in the ore is continuously leached, and no new ore is continuously added, so there is no real steady state. Australia Jili Lang stretch (Gililambone) is a medium-sized ore mine in ore 750,000 t, copper producing 7500t. The copper recovery rate as a function of time from the leaching solution, starting 40 days, is the first stage, and the copper recovery rate rises almost linearly up to about 50% . Then enter the easing rise, the final recovery rate rose to about 90% in 230 days . The table below lists the main parameters of the plant's heap leaching, as well as the parameters of the large copper plant in St. Manuel ( 54,000 tons of copper per year) .

   Building a mathematical model that describes the leaching heap is very helpful in controlling and predicting the operation of the heap. Although theoretically, the rate of leaching of a nugget depends on the rate of diffusion within the pores of the ore and the volume of the nugget, it should be described by a shrinking core model. In actual operation, the leaching speed of the pile is related to the flow rate of the leachate. Some mines use the mathematical model of the empirical equation to simulate the change of the leaching rate of the whole pile. The following describes a simple model form: [next]
Leach rate % = CF v
   Where C is a constant associated with the total amount of soluble copper in the ore, related to the pile height, and the pile height
F—— the cumulative flow rate of the leachate applied to each ton of ore, in kL/t ;
v - the index of F , called the ore leaching speed variable. For an oxidized ore v was determined to be 0.3470 .
   When applying the model, you can select a unit of the heap, the size of the input unit, the flow of the leachate, and so on. The figure below is an estimate of the leaching life of the model for column leaching and different stack heights.

A common problem in heap leaching operations is the accumulation of water at the top, which tends to cause channeling and increases the hydrostatic head at the bottom of the pile. Plowing the top ore and removing the crust, mud or salt can improve the top seepage capacity, increase the leaching speed and rich liquid concentration, and thus shorten the total leaching time. Different methods of tilling should be adopted due to different piping methods. If the pipe distance is large, a bulldozer can be used. If the pipe spacing is small, it may be necessary to use labor, or remove the pipe network and then plow.
Many factories and mines periodically discharge and rest in actual operation, with a period of several days. This not only reduces the accumulation of water, but also facilitates the contact of ore with air, which is especially important for ore heap leaching of sulfide ore.
Reconstruction of pile
    As the leaching progresses, the decomposition and pulverization of some ore blocks often cause the pile to naturally sink and collapse. The sinking speed is closely related to the composition and nature of the ore. When the soluble copper in the ore has been extremely reduced, the leaching speed is very slow, and the life of the heap is gradually reaching the end. However, when the leaching is terminated, the factors of recovery rate and time should be weighed to make judgments. [next]
After the heap is terminated, it is generally necessary to build a new heap on it. Shengmanniuer practice mine is first removed from the top of the stack pipe network, and then re-plowing with a bulldozer to the two vertical and horizontal directions to 0.8
Technical improvement of heap leaching
   A ore pellet - ripening
When the ore is broken, some powder ore will be produced. Directly adding to the heap will reduce the gap in the heap and even cause the channel and air to not circulate. One solution is to pellet the pellets with a small amount of binder, such as cement, into a pellet, solidified and then heap immersed.
In order to improve the leaching speed of the pellets, many of the plant's concentrated sulfuric acid and high-iron-containing raffinate are added to the ore powder to make the ball. The pellets are generally wet at 8% to 10% . The heat generated by the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with water contributes to the reaction of copper with acid, and the high iron also contributes to the oxidative dissolution of natural copper and chalcopyrite in the ore. The pellets need to be placed for two or three days before they are piled up. This whole process is called " maturing . " The first to use this approach is that the US car Cyprus Ruth Miami (Cyprus Miami) copper mine.
   B surfactant
The St. Manuel mine adds surfactant to the heap immersion liquid to reduce surface tension and promote penetration of the solution into the pores of the ore. The difficulty in selecting a surfactant is that the surfactant needs to adapt to the strong acidic environment of the leachate, and it must not adversely affect the solvent extraction process. With the help of researchers from the US Bureau of Mines, the mine selected a cationic fluorocarbon surfactant after years of research and comparison.
references
   1 Kelly RJ , Zarate , Copper95 743-755Biswas AK , Davenport WG , Extractivemetallurgy of Copper , Peragmon Press , Oxford , ed
   2 James , B , Lancaster.T , ALTA , 1998 , Copper , Hydrometallurgy , Forum , Oct , 20-21 , 1998 , Queensland , Australia
   3 Jenkins JG , Mining Eng . 1994 , Sep. 1094~1098
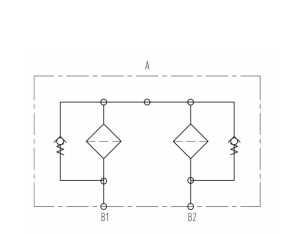
SDRFD filter consists of one-piece housings with a bolt-on cover plates. The two housings are connected by a ball change-over valve. There are clogging indicators on both sides.
Symbol for hydraulic systems
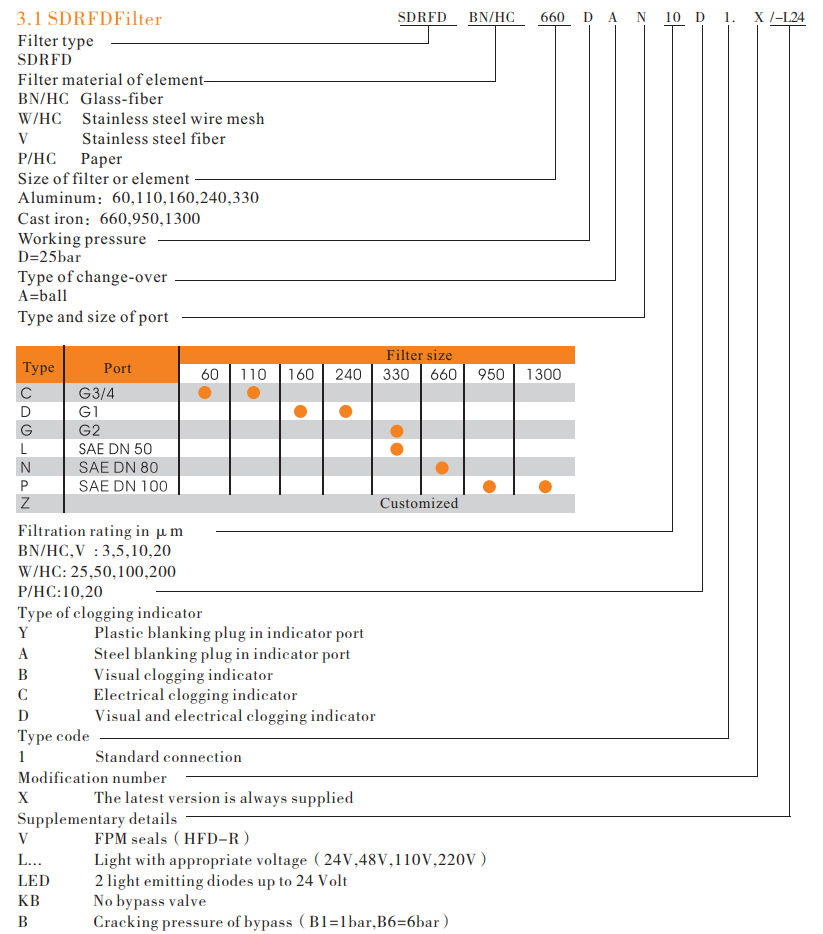
Filter elements are available with the following pressure stability values:
BN/HC: 25 bar
Paper(P/HC): 10 bar
Wire mesh( W/HC ): 30 bar
Stainless steel fiber( V ): 30 bar
Compatibility
It can be used for mineral oils, lubrication oils, non-flame fluids, synthetic and rapidly biodegradable fluids. For water or other application, please contact us.
General
Mounting
Tank-top mounted or inline filter.
Flow
Inlet: by a ball change-over valve
Outlet: down
Temperature range
-10℃~100℃(others on request)
Pressure setting of clogging indicator
â–³Pa=2bar-0.2bar (others on request)
Bypass cracking pressure
â–³Po=3bar-0.5bar (others on request)
Model code
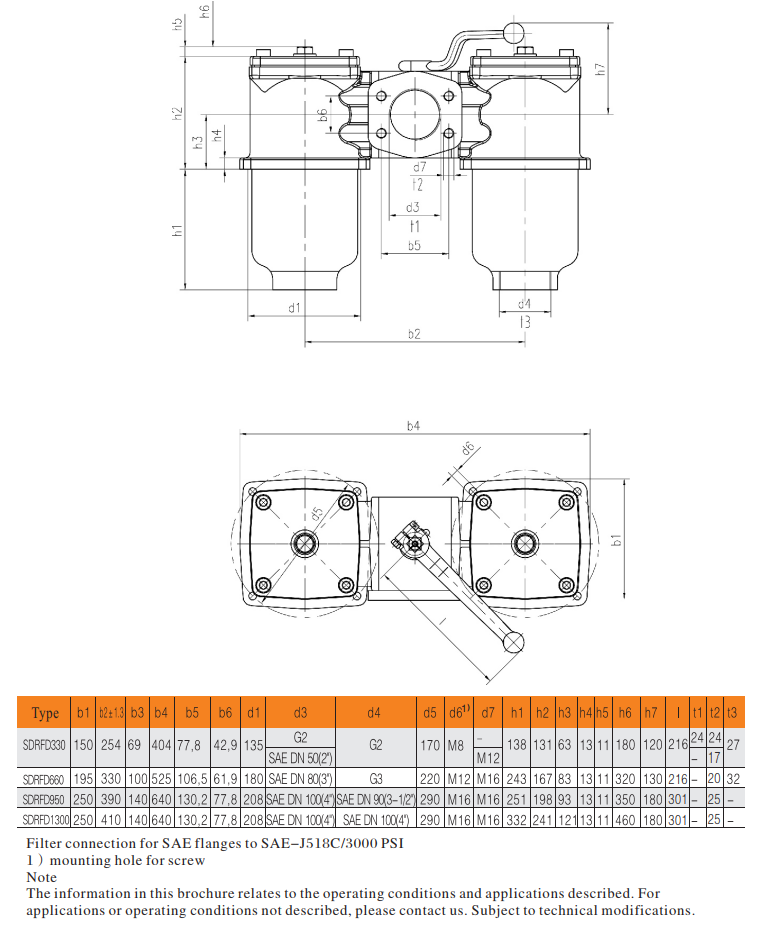
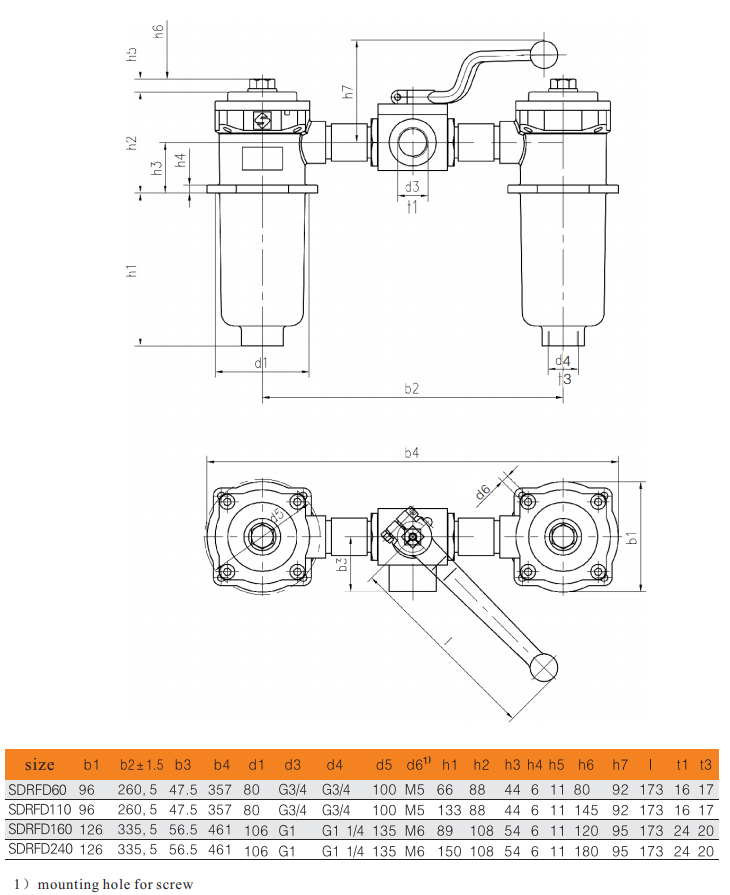
Filter Dimension
Excavator Filter,Double Housing Filter,Housing Filter,Filter Housing
Xinxiang Shengda Filtration Technique Co., Ltd. , https://www.filtrations.nl